In UV inkjet printing, most technical issues originate from ink formulation and material compatibility. Understanding how UV ink quality is defined helps printers, integrators, and brand owners avoid costly failures and achieve consistent results. Below are the seven core criteria used to evaluate industrial-grade UV-curable inks.
Resins determine adhesion, flexibility, hardness, and scratch resistance. Polyurethane acrylates are ideal for flexible substrates, epoxy acrylates provide high hardness and gloss for rigid materials, while polyester acrylates balance both properties. High-end UV inks typically use imported resins with solid content above 95% and stable molecular weight distribution to ensure consistent curing and durability.
Monomers directly affect ink flow, viscosity, odor, and film formation. Monofunctional monomers improve penetration and jetting, while multifunctional monomers enhance hardness and abrasion resistance. Professional UV ink formulations rely on blended monomer systems to balance printability, mechanical strength, and long-term stability.
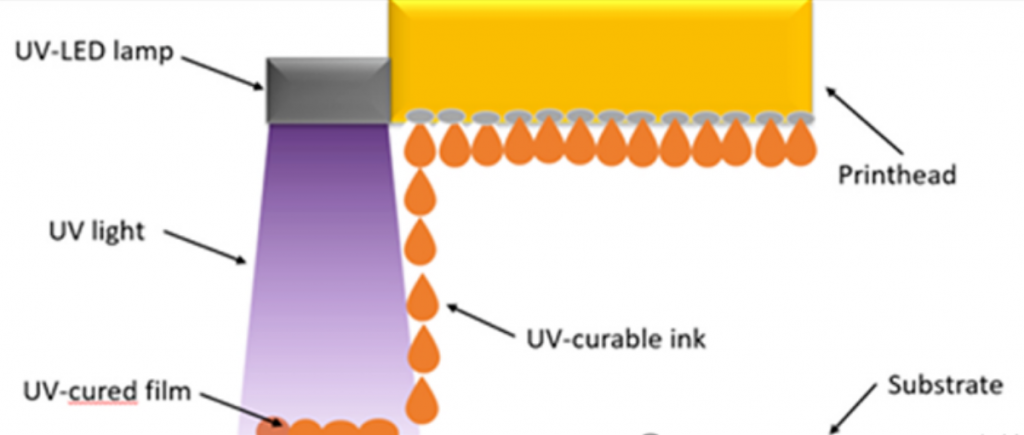
Photoinitiators define curing speed and curing depth. Industrial UV inks commonly use imported TPO or 819-series photoinitiators, enabling curing in under one second with deep curing thickness of 80–120 microns. This ensures full polymerization, strong adhesion, and resistance to aging.
High-quality UV inks require uniform pigment dispersion between 150 and 300 nanometers. Inkjet-grade pigments eliminate large particles and agglomerates, ensuring high color saturation, smooth gradients, and long-term storage stability without sedimentation or nozzle clogging.
Final filtration accuracy of 0.2–0.5 microns is essential to protect industrial printheads. Advanced stabilizer, defoamer, and surfactant systems prevent foaming, ink separation, and premature resin crosslinking, ensuring reliable jetting during long production runs.
Premium UV inks deliver a color gamut 5–20% wider than standard OEM inks, with ΔE values below 2 for industrial printing. Advertising applications prioritize vivid colors and high density, while packaging and industrial markets focus on color consistency and batch stability.
Outdoor durability depends on resin structure, pigment UV resistance, and photoinitiator stability. Industrial UV inks withstand 500–1000 hours of QUV aging, maintain low yellowing values, and resist chemicals such as alcohol, cleaners, sweat, salt spray, and mild acids or alkalis.
UV inks must be compatible with mainstream printheads including Epson, Ricoh, Konica Minolta, Kyocera, and Seiko. Stable viscosity, matched surface tension, non-corrosive pH levels, and continuous 8–12 hour printing without dropouts are mandatory for industrial use.
In the inkjet industry’s razor-and-blade business model, ink quality directly determines long-term competitiveness.
#UVInk #UVCurableInk #IndustrialUVInk #UVInkQuality #UVInkFormulation #UVInkjetInk #UVInkAdhesion #UVInkColorGamut #UVInkWeatherResistance #InkjetPrinting


2022-08-03


2025-01-06

